Mineral processing is the backbone of the modern mining industry, transforming raw ores into valuable concentrates while addressing economic, environmental, and technological challenges. With declining ore grades and stricter sustainability regulations, optimizing beneficiation processes has never been more crucial. This guide provides a step-by-step breakdown of ore beneficiation, from preparation to environmental management, along with cutting-edge solutions driving efficiency and sustainability.
Point 1: Overview of Ore Beneficiation
Ore beneficiation refers to the process of separating valuable minerals from waste rock (gangue) through physical, chemical, or biological methods, improving ore grade to meet smelting or industrial requirements. It serves as a critical link between mining and metallurgy, directly impacting resource utilization, production costs, and environmental sustainability.
Core Objectives of Ore Beneficiation
- Concentrate valuable elements(e.g., copper, iron, lithium, gold)
- Remove harmful impurities(e.g., sulfur, arsenic, silica)
- Reduce smelting costs(less transportation and processing of waste material)
- Maximize resource utilization(make low-grade ores economically viable)
Importance of Ore Beneficiation
Ore beneficiation plays an irreplaceable role in mining production, primarily manifested in the following four aspects:
(1) Economic Benefits
- Increases concentrate grade, reducing energy consumption in subsequent smelting (e.g., transporting 1 ton of 30% copper concentrate saves 80% cost compared to 5% raw ore).
- Transforms low-grade ore into usable resources (e.g., making 0.3% copper ore economically viable).
(2) Resource Sustainability
- Minimizes mineral waste, extending mine lifespan.
- Enhances recovery rates (e.g., copper flotation recovery can reach 85%~95%).
(3) Environmental & Energy Benefits
- Reduces tailings discharge(e.g., via dry stacking technology).
- Replaces high-pollution methods (e.g., bioleaching instead of cyanidation for gold extraction).
(4) Industrial Applicability
- Meets purity requirements for various industries (e.g., battery-grade lithium concentrate requires≥6% Li₂O).

Point 2: Basic Process Flow for Mineral Ore Beneficiation
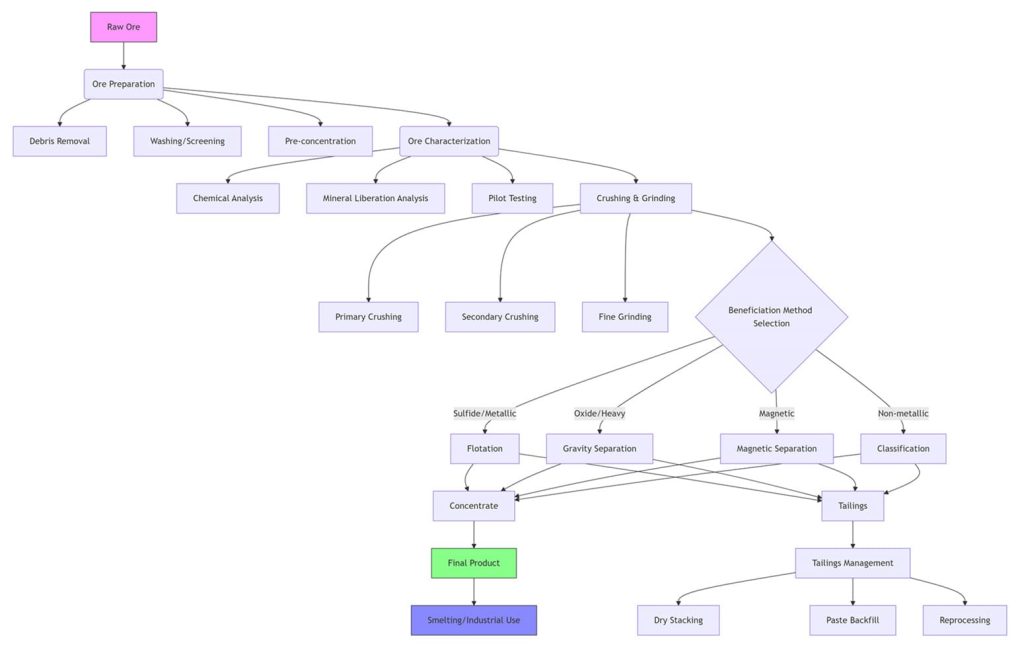
Ore beneficiation is a complex process involving multiple critical steps, each impacting final recovery rates and economic returns. Below is a detailed description of the key steps:
1. Ore Preparation
Ore preparation is the first step in the beneficiation process, primarily involving material collection, transportation, and preliminary screening. This step aims to remove large waste rock and soil, providing higher-purity feedstock for subsequent processing.
Primary Operations
- Debris Removal: Eliminate large waste rock and soil (e.g., manual sorting, screening).
- Ore Washing: Rinse away clay and dust (spiral washers, vibrating screens).
- Pre-concentration: Early waste rock removal using XRT intelligent sorting or photoelectric separation.
Challenge: High-moisture-content ore prone to equipment clogging.
2. Ore Characterization & Testing
Detailed analysis and evaluation of raw materials before actual processing is critical, with the core objective being to determine ore recoverability. Analysis and evaluation encompass chemical composition analysis and physical property testing to customize an optimized beneficiation plan, ensuring maximum recovery of valuable minerals.
Key Methods
- Chemical Analysis (XRF/XRD):Determines elemental content and mineral composition.
- Mineral Liberation Analysis (MLA): Studies grain size distribution and liberation degree.
- Pilot/Semi-Pilot Testing:Simulates industrial processes (e.g., flotation column tests).
Key Parameters: Ore hardness (Bond Work Index), embedding characteristics, distribution of valuable components.
3. Crushing & Grinding
The core function of crushing and grinding is to liberate target minerals and achieve individual liberation. This process mechanically reduces the size of large ore lumps, creating conditions for downstream processing. Crushing is typically performed using jaw crushers or gyratory crushers, while grinding is usually carried out with ball mills or rod mills. Finer particles facilitate more efficient separation in subsequent steps.
Typical Process
- Primary Crushing– Jaw Crusher (to 100-200mm).
- Secondary Crushing – Cone Crusher (to 20-50mm).
- Fine crushing– High-pressure roller mill (HPGR) or impact crusher.
- Grinding– Ball mill/rod mill (P80 to 75-150μm).
Trend: Ultrafine grinding (vertical mills) for difficult-to-process ores like nickel/spodumene.
4. Beneficiation Methods
Common beneficiation methods include gravity separation, flotation, and magnetic separation. Gravity separation utilizes density differences to separate materials through gravitational forces. Flotation employs the immiscibility of oil and water; by adding frothing agents, specific minerals attach to bubbles and float to achieve separation. Magnetic separation leverages the differing magnetic properties of materials, using magnetic fields to separate magnetic from non-magnetic substances.
Selecting techniques based on mineral properties:
| Mineral Type | Applicable Method | Example Minerals |
| Sulfides/Metallic Ores | Floating (Xanthates as collectors) | Copper, Lead-Zinc, Molybdenum |
| Oxides | Gravity Separation(Shaking Tables/Spiral Chutes) | Cassiterite, Wolframite |
| Magnetic Minerals | Strong Magnetic Separation/Weak Magnetic Separation | Magnetite, Ilmenite |
| Light Non-metallic Minerals | Air Classification or Electrostatic Separation | Quartz, Feldspar |
Key Metrics: Recovery Rate, Concentrate Grade, Enrichment Ratio.
5. Advanced Technologies & Equipment
Automated Control Systems
Advanced automated control systems play a vital role in mineral processing. These systems enhance operational efficiency, minimize operational errors, and continuously optimize production processes based on real-time monitoring data, thereby boosting overall production efficiency.
High-Efficiency Energy-Saving Equipment
High-efficiency energy-saving equipment, such as high-frequency screens, vertical mills, and new flotation machines, offers significant advantages in both energy consumption and metal recovery rates. They reduce energy consumption, increase output efficiency, and lower operational costs.
Advanced Mineral Processing Technologies & Equipment Breakthroughs
Sensor-Based Sorting
- X-ray Transmission (XRT) – Sorts diamonds/lithium ore.
- Near-Infrared (NIR) – Identifies spodumene from feldspar.
High-Efficiency Flotation Equipment
- Jameson Flotation Cell – 50% energy savings, 5% recovery rate increase.
- Column Flotation Machine – Suitable for ultrafine minerals.
Bioleaching|: Microbial extraction of low-grade copper/gold.
Point 3: Challenges & Solutions in Mineral Processing
Mineral processing is critical for enhancing the value of ore resources, yet it often faces challenges such as grade fluctuations, complex mineralogy, high energy consumption, and environmental pressures. Below, we analyze key issues and modern solutions across various fields.
1. Challenges Due to Variable Ore Characteristics
Issues
- Declining Ore Grades(e.g., copper ores <0.5%, iron ores <20%), reducing economic viability.
- Complex Mineralogy(fine-grained inclusions, mixed oxide-sulfide ores).
- Harmful Element Interference(arsenic, sulfur, and silicon affecting smelting).
Solutions
Pre-concentration & Waste Rejection
- XRT/NIR Sensor-Based Sorting: Rejects 30%~60% waste rock upfront, lowering grinding costs (40% energy reduction in South African diamond mines).
- Dense Media Separation (DMS): Separates minerals with significant density differences (e.g., tungsten, spodumene).
Precision Process Design
- Stage Grinding-Stage Separation: Prevents overgrinding (e.g., porphyry copper ores use coarse grinding → roughing → regrinding).
- Integrated Flowsheets: Combines flotation + magnetic separation + leaching for complex polymetallic ores (e.g., Pb-Zn-Ag deposits).
2. Low Separation Efficiency Challenges
Issues
- Poor Recovery of Ultra-Fine Particles(<10 µm particles easily lost).
- Difficulty Separating Similar Minerals(e.g., galena/sphalerite, quartz/feldspar).
Solutions
Advanced Reagents & Flotation Optimization
- Selective Collectors: Eco-friendly alternatives (e.g., thioglycolate replacing xanthate).
- Nano-Bubble Flotation: Enhances fine particle adhesion (pilot trials show +15% Cu recovery).
Enhanced Physical Separation
- High-Gradient Magnetic Separation (HGMS): Recovers weakly magnetic minerals (e.g., ilmenite, hematite).
- Microwave Pretreatment: Alters mineral surface properties (accelerates gold cyanidation).
3. Energy & Cost Pressures
Issues
- Grinding consumes 50%~70% of plant power(Bond Work Index Wi impacts costs).
- High Reagent Costs(e.g., lithium ore collectors account for 30% of OPEX).
Solutions
Energy-Efficient Equipment
- High-Pressure Grinding Rolls (HPGR): Replaces ball mills, saving 20%~30% energy (Chilean copper mines).
- Tower Mills: Reduce fine grinding energy by 40%.
Alternative Processes & Circular Economy
- Bioleaching: Low-grade Cu/Au heap leaching (avoids crushing/grinding).
- Tailings Reprocessing: Recovers REEs, phosphates (e.g., Bayan Obo tailings reprocessing).
4. Environmental & Tailings Challenges
Issues
- Tailings Dam Failures(10+ major global incidents in recent years).
- Heavy Metals/Cyanide in Effluents(e.g., gold cyanidation wastewater).
Solutions
Zero-Waste Mining
- Dry Stacking + Eco-Rehabilitation: Reduces dam usage (Zijin Mining case study).
- Paste Backfilling: Mixes tailings with binders for underground voids.
Green Reagents & Closed-Loop Water
- Cyanide-Free Gold Extraction(thiosulfate/thiourea leaching).
- Membrane Treatment: Enables zero liquid discharge (ZLD).
In practical operation, common problems such as equipment wear and excessive reagent consumption can be solved through regular maintenance and optimization of reagent formulations. Simultaneously, strengthening employee technical training can effectively prevent operational errors and improve production efficiency. Methods to improve recovery rates include optimizing the process flow, using more advanced equipment, and adding highly effective reagents. Furthermore, using multi-stage recovery techniques can further increase the recovery rate of rare metals and precious elements, maximizing resource utilization.

Point 4: Environmental Protection Measures in Mineral Processing
As environmental awareness grows, implementing effective protection measures during ore beneficiation has become essential. These include wastewater treatment, exhaust gas purification, and solid waste management, to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainable development.
1. Wastewater Treatment
Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) Control
- Neutralization (e.g., lime/limestone treatment to pH 7–9).
- Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) for heavy metal precipitation.
Recycling & Reuse
- Closed-circuit water systems reduce freshwater consumption.
- Membrane filtration (reverse osmosis) for high-purity reuse.
Tailings Water Treatment
- Sedimentation ponds + coagulants (e.g., polyacrylamide).
- Electrocoagulation for dissolved pollutants.
2. Exhaust Gas Purification
Dust Suppression
- Wet scrubbers & bag filters (removal efficiency >99%).
- Fog cannons/mist sprays in crushing zones.
SO₂ & NOx Reduction (from roasting/smelting)
- Scrubbers (limestone slurry for SO₂ absorption).
- Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for NOx.
Mercury & VOC Control (gold processing)
- Activated carbon adsorption.
- Condensation systems for Hg recovery.
3. Solid Waste Management
Tailings Disposal
- Dry stacking(reduces water use, prevents dam failures).
- Paste thickening(~70% solids) for safer storage.
- Backfilling abandoned mines(stabilizes voids).
Slag & Waste Rock Utilization
- Construction materials (e.g., cement additives, aggregates).
- Mine-site rehabilitation (landscaping, soil amendments).
Point 5: Future Development Directions and Trends
Technological Innovation and Breakthroughs
In the future, technological innovation and breakthroughs will continue to drive progress in the field of mineral processing. With the application of technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics, processing efficiency and accuracy are expected to see significant improvements, opening up new possibilities for the industry.
Environmental Protection and Sustainable Development
Environmental protection and sustainable development are central themes for future growth. Introducing green technologies, reducing pollution emissions, and achieving efficient resource utilization will become key directions for advancing the industry.
Conclusion
As mining faces declining ore grades, stricter environmental regulations, and rising energy costs, the beneficiation industry must adapt with smart technologies, sustainable practices, and optimized processes. From AI-driven sorting to zero-waste tailing solutions, the future of mineral processing lies in innovation and efficiency. Whether upgrading an existing plant or designing a new operation, implementing these strategies can boost recovery rates, cut costs, and minimize environmental impact.
Ready to optimize your beneficiation process? Contact our experts today for customized mineral processing solutions!



